Celiac Disease: The New Terror
Celiac
Disease, literally known as gluten allergy, is a serious
lifelong auto immune disorder. Two and a half million Americans remain
undiagnosed.
In this, the patient
develops immune responses against gluten protein attacking the small intestine
thereby reducing the absorption of nutrients from food. This is most common in
Caucasians but now found globally. The rate of incidence is 1 in 100 worldwide.
What
is Gluten?
Gluten
is
a protein found in wheat, rye and barley. Ingestion of these grains triggers cellular
immune responses, development of antibodies against gluten protein, damaging
the lining of small intestine. Small finger-like projections, micro-villi, line the small intestine.
Antibodies generated in response to gluten protein damage these tiny projections
hampering optimal absorption of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients from
food.
3
W’s: When, Whom and Why
Celiac can develop at
any age once humans start eating foods and medicines containing gluten. But individuals
with following are at an elevated risk:
- · Type 1 Diabetes
- Celiac running in families or hereditary celiac
- Down syndrome/Turner’s syndrome
- Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Addison’s Disease
Celiac tends to run in
families. Being a genetic disorder occurs primarily due to interaction between
genes, it can be passed on from parents to progeny. Celiac might also be a joint
effect of several environmental factors, surgery, pregnancy, child birth, viral
infection or severe emotional stress.
Signs
and Symptoms
Celiac is difficult to
diagnose as it manifests in varied manner in different people. More than 200
celiac symptoms have been observed. Some develop celiac as a child and some as
an adult, also many individuals positive for celiac show no symptoms at all.
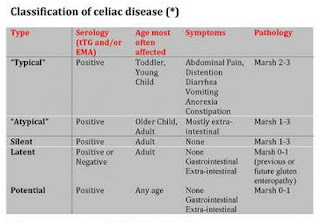
Types
of Celiac Diseases
World Gastroenterology
Organization has categorized celiac into three classes:
Associated
Diseases
1. Dermatitis Herpetiformis
§ Itchy
blistering skin disease that stems from intestinal gluten intolerance
§ Rashes
occur on knees, torso, buttocks, scalp and elbows
§ Changes
in villus lining of small intestine
2.
Type
1 Diabetes
When
to see a Doctor
Consult a doctor on
experiencing diarrhea or digestive discomfort. In case of children, when a
child is pale, irritable, failing to grow, surfacing potbelly and bulky stools
indicates need for medical supervision.
Complications
· Malnutrition
· Loss of Ca+2 and bone
density
· Infertility and miscarriage
· Lactose Intolerance
· Neurological Disorders
· Skin Disorders
· Cancer
Screening
There are several serological (blood) tests available that screen for
celiac disease antibodies, but the most commonly used is called a tTG-IgA test.
For this test to work, you must be
consuming gluten. This test detects the formation of gluten antibodies in
individual’s blood. If blood test results suggest celiac disease, your
physician will recommend a biopsy of your small intestine to confirm the
diagnosis.










Comments
Post a Comment